Rubber sealing stripes are an essential component in many industrial, commercial, and residential applications where a tight and effective seal is required against water, air, dust, and other environmental elements. The main functions of rubber sealing stripes can be broadly categorized into three areas: sealing, insulation, and protection.
(1)Sealing: One of the primary functions of rubber sealing stripes is to prevent leaks, drafts, and energy loss. Rubber sealing stripes are designed to be compressed tightly against the surfaces they are sealing, creating a barrier that prevents the ingress of unwanted elements, such as water, air, dust, and insects. In addition to providing an effective seal against environmental elements, rubber sealing stripes can also prevent noise and vibration transmission, which is particularly important in applications where a quiet and comfortable environment is required.
(2)Insulation: Rubber sealing stripes also provide insulation properties, which can help to reduce energy loss and improve energy efficiency. By creating an airtight seal, rubber sealing stripes can prevent heat transfer through convection and conduction, reducing the amount of energy required to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. Rubber sealing stripes can also improve thermal insulation and soundproofing, which is particularly important in applications such as refrigeration units, sound studios, and home theater rooms.
(3)Protection: Rubber sealing stripes can also provide protection against impact and abrasion damage. In applications where components are frequently moved or subjected to external forces, such as doors, cabinets, and enclosures, rubber sealing stripes can act as a cushion, absorbing the impact and protecting the surfaces from damage. Rubber sealing stripes can also be used to protect delicate equipment and machinery from dust and debris, which can cause damage and reduce the lifespan of the equipment.
Rubber sealing stripes are available in a wide range of materials, shapes, and sizes to suit a variety of applications. Some of the most common materials used in rubber sealing stripes include EPDM, neoprene, silicone, and nitrile. Each material has unique properties that make it suitable for specific applications, such as temperature resistance, chemical resistance, and durability.
Microwave vulcanization is a one-time forming process that is used to cure rubber compounds. This process uses microwave energy to generate heat within the rubber compound, causing it to cure quickly and efficiently. The process can be used for a wide range of rubber products, including automotive parts, medical devices, and consumer goods.
Microwave vulcanization offers several advantages over other curing methods. One of the primary benefits is the speed of the process. Unlike traditional curing methods, which can take several hours or even days, microwave vulcanization can cure a rubber compound in a matter of minutes. This means that manufacturers can produce rubber products much faster, resulting in increased productivity and lower costs.
Another advantage of microwave vulcanization is the uniformity of the curing process. Traditional curing methods often result in uneven curing, which can lead to defects and inconsistencies in the finished product. Microwave vulcanization, on the other hand, provides a more uniform and controlled cure, resulting in higher quality and more consistent products.
The microwave vulcanization process also requires less energy than traditional curing methods. This is because the microwave energy is absorbed directly by the rubber compound, rather than heating the entire mold or curing chamber. This reduces energy consumption and makes the process more environmentally friendly continues to advance, it is likely that microwave vulcanization will become even more prevalent in the production of rubber products.
The EPDM sealing strip produced by us adopts a microwave vulcanization process for one-time molding, the surface is smooth and beautiful, and it has good elasticity and compression deformation resistance.










 English
English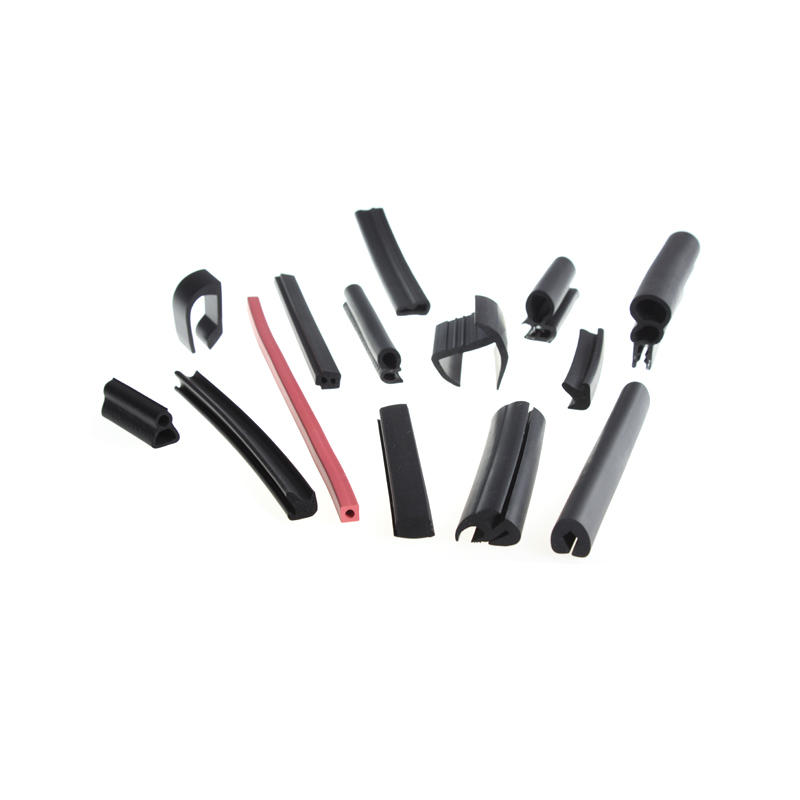
.jpg?imageView2/2/format/jp2)
.jpg?imageView2/2/format/jp2)
.jpg?imageView2/2/format/jp2)
.jpg?imageView2/2/format/jp2)

.jpg?imageView2/2/format/jp2)
